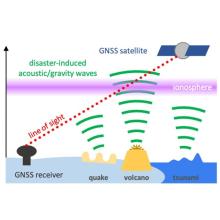
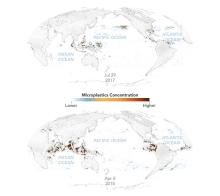
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is the U.S. version of a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). A GNSS system like GPS has three components: satellites in well-known orbits with synchronized clocks, ground controllers, and a ground segment providing data to users. Using signals from four satellites, a precise location in three-dimensions (within millimeters or less) along with precise time can be determined. By comparing measurements over time, minute elevation and distance changes at a station can be calculated.