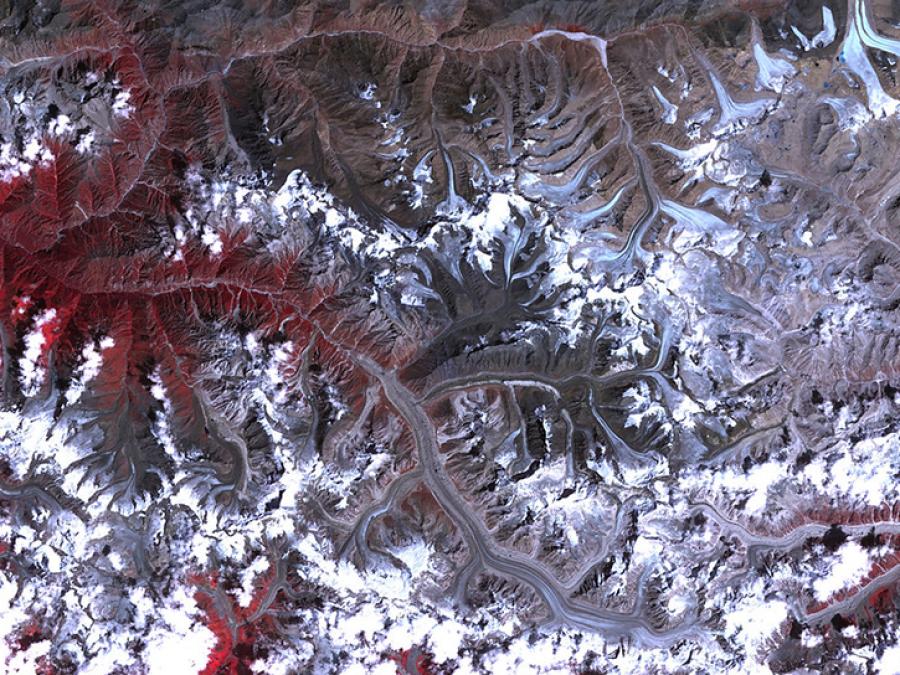
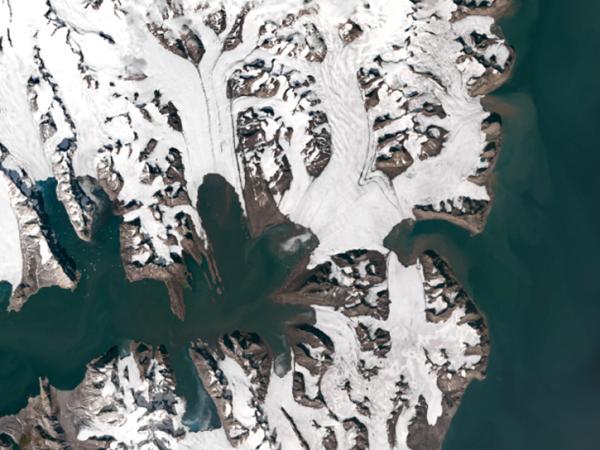
The GLIMS Glacier Database was created using data contributions from many glaciological institutions, which are managed by Regional Coordinators who coordinate the production of glacier mapping results for their particular region. The GLIMS Glacier Database provides students, educators, scientists, and the public with reliable glacier data from these analyses. New glacier data are continually being added to the database.
Data Attribute Summary
Parameter: Glacier Extent
Platforms: Landsat, Terra
Sensors: ETM+, ASTER
Data Formats: WMS, WFS, GML, ASCII, Shapefile, KML
Temporal Coverage: January 1, 1850, to present
Temporal Resolution: Not applicable
Spatial Resolution: Varies
Spatial Reference System: WGS 84
Spatial Coverage: Global