Introduction
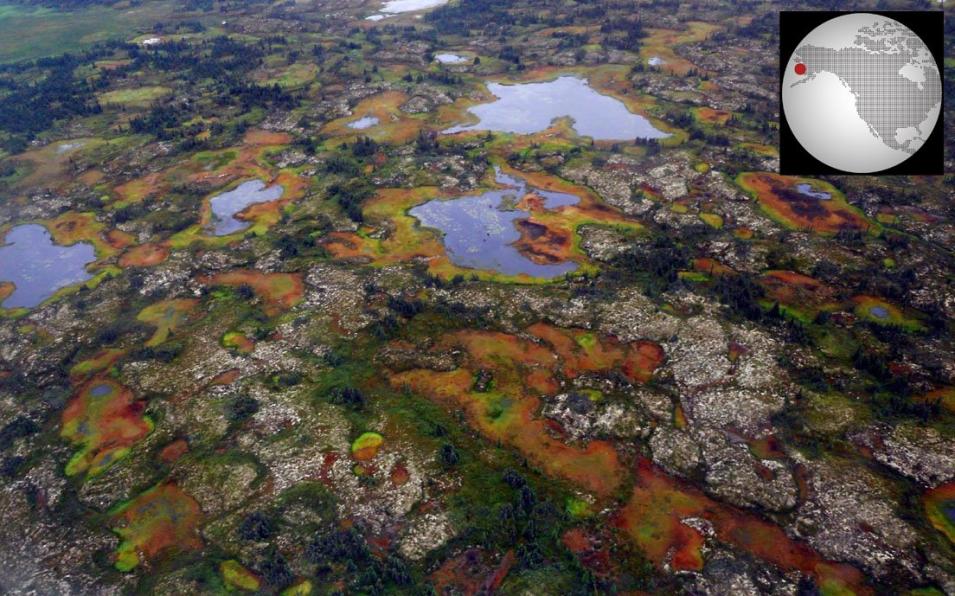
The distribution of permafrost is generally poorly mapped at regional scales. This presents a problem for resource managers and modelers trying to understand the distribution and extent of permafrost susceptible to a warming climate. To better understand permafrost’s influence on high-latitude ecosystems, researchers are developing methods to map the presence of permafrost.
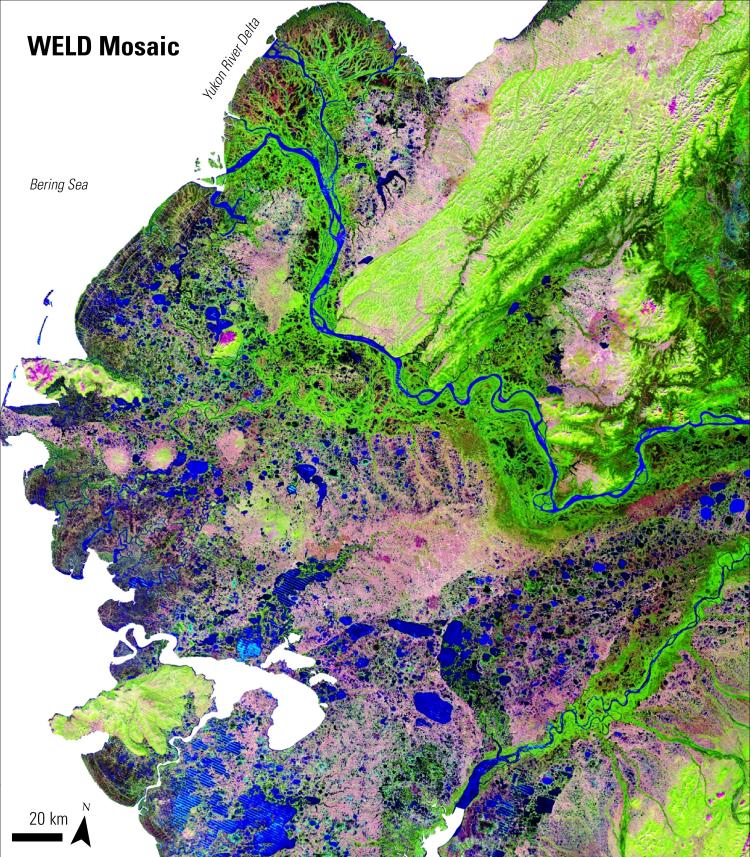
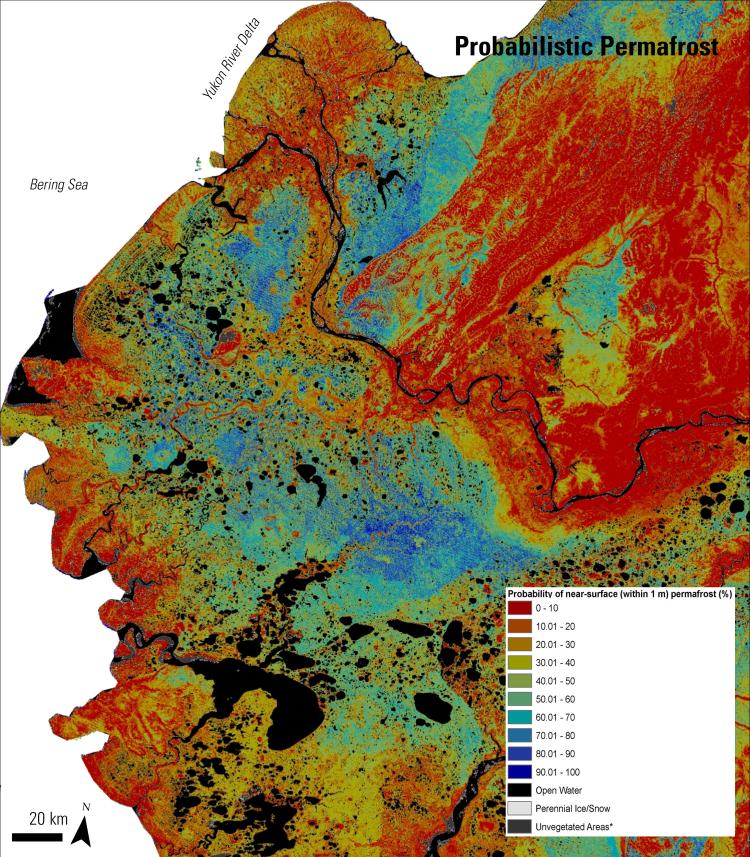
In a 2014 study published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, researchers incorporated field observations, remotely sensed data, biophysical variables, and a decision tree statistical model to produce a probabilistic map of near-surface (defined, in this study, as within 1 meter of the Earth’s surface) permafrost distribution within the Yukon River Basin of Alaska.