Background
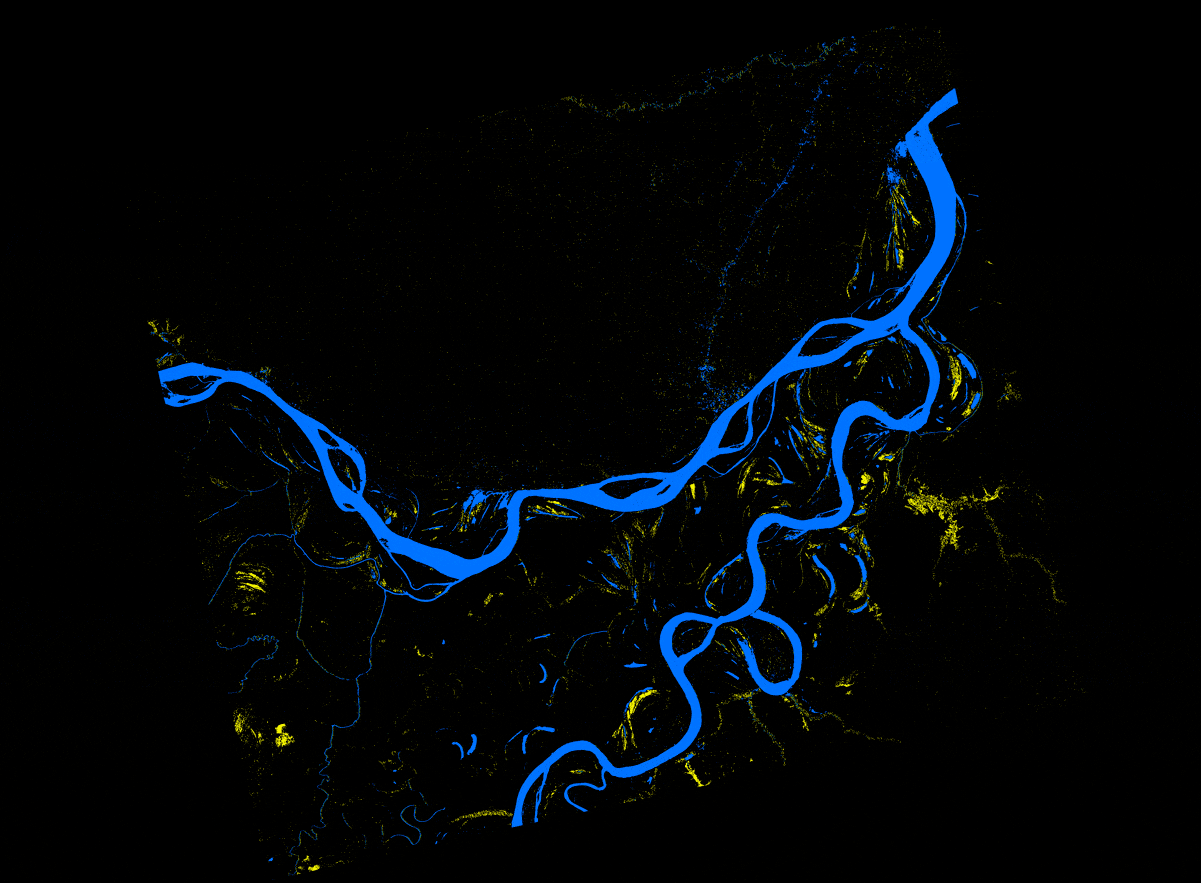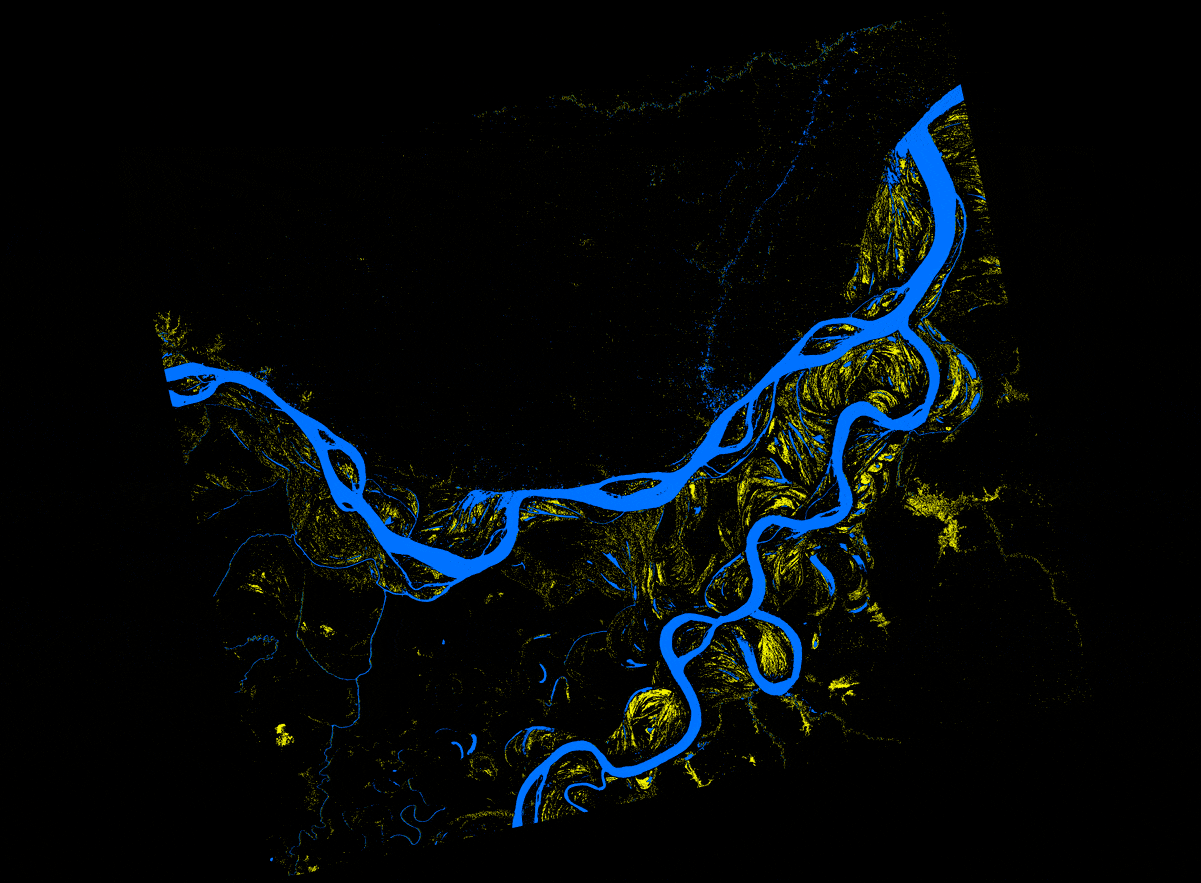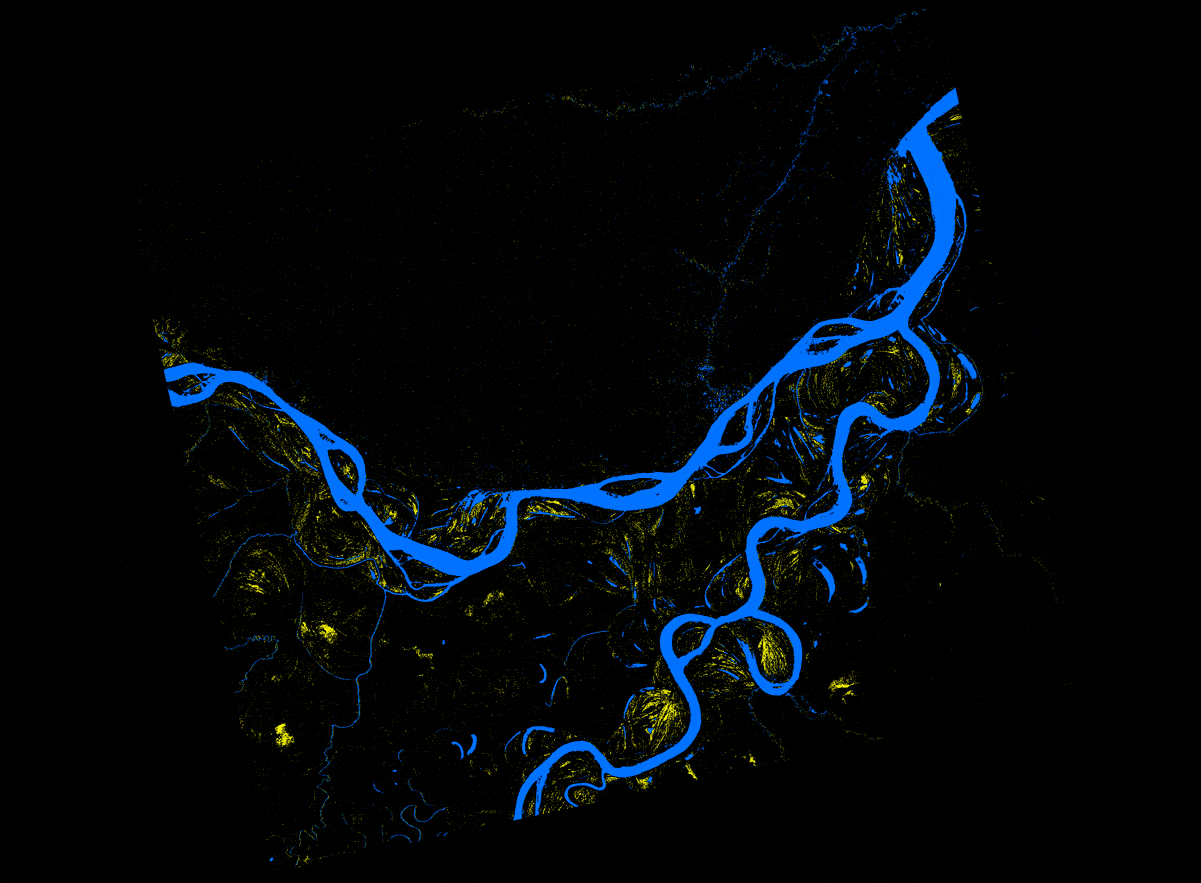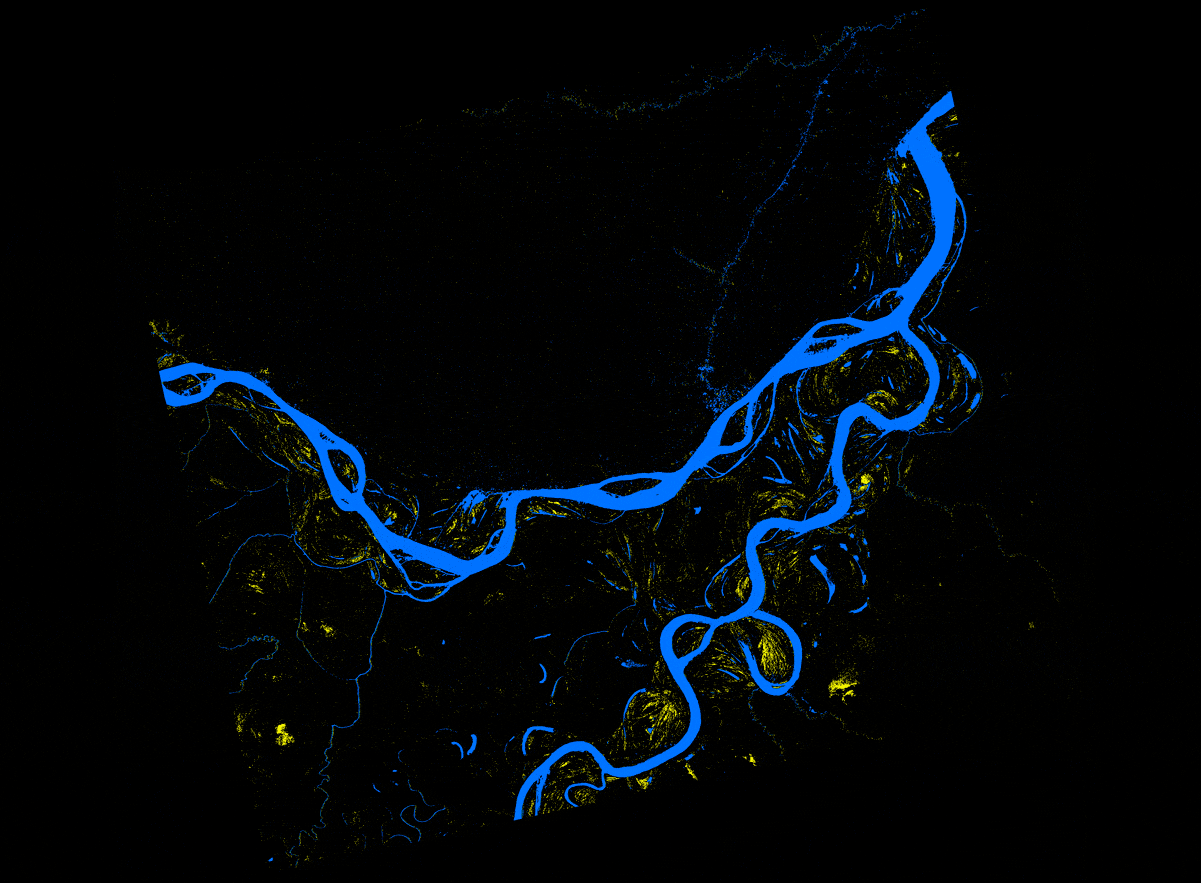
The all-weather ability of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) to penetrate cloud cover and low-light conditions to acquire imagery of the Earth’s surface is well known. Given the recent availability of high-resolution terrain models at 30 meters from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) and an interest to make SAR data easier to use, the Alaska Satellite Facility (ASF) now offers radiometric terrain corrected (RTC) L-band image products from Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) Phased Array L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) data. At longer wavelengths such as L-band, SAR can penetrate surface vegetation including the Amazon rain forest, and flooding events can be mapped very accurately at high resolution. With the availability of RTC data, it is now relatively easy to do accurate flood mapping using PALSAR data.
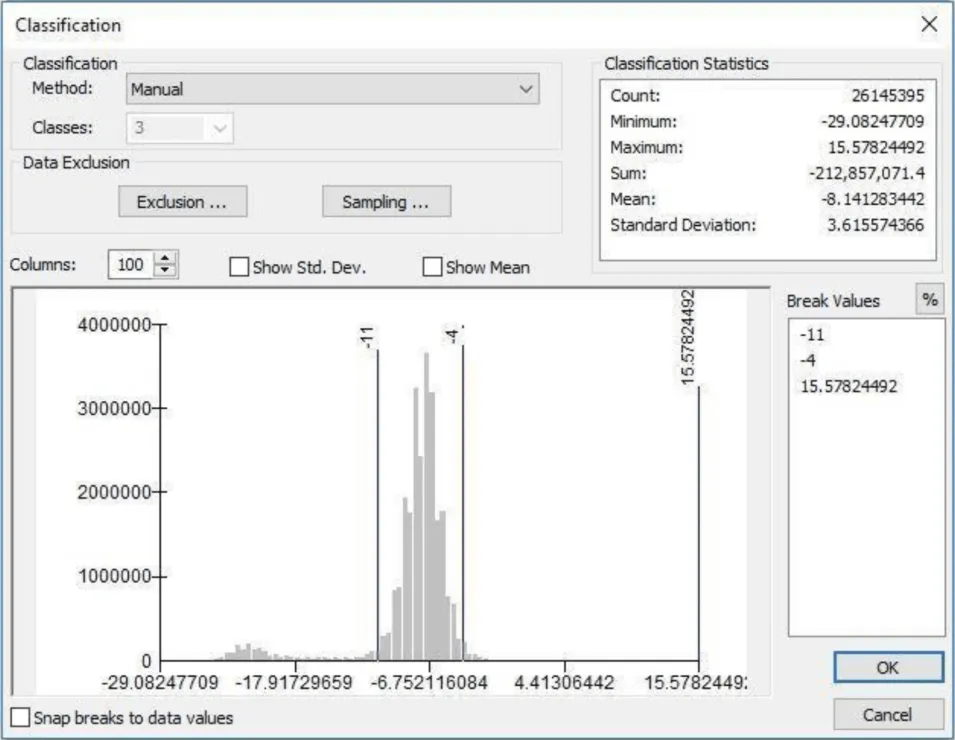
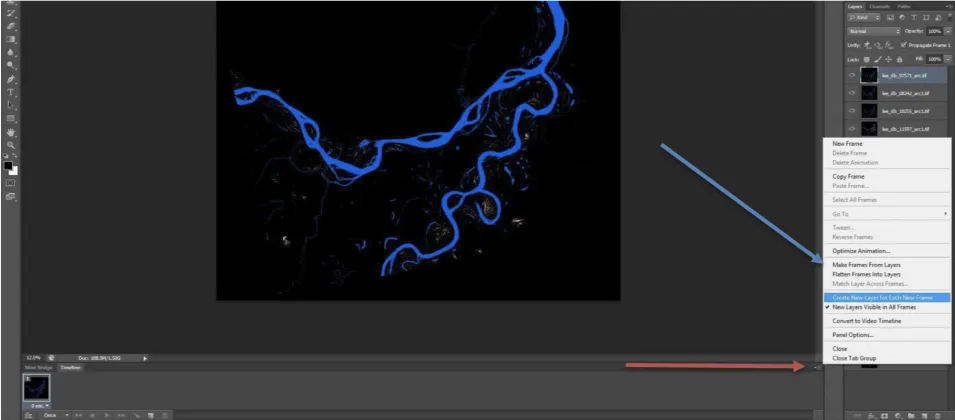
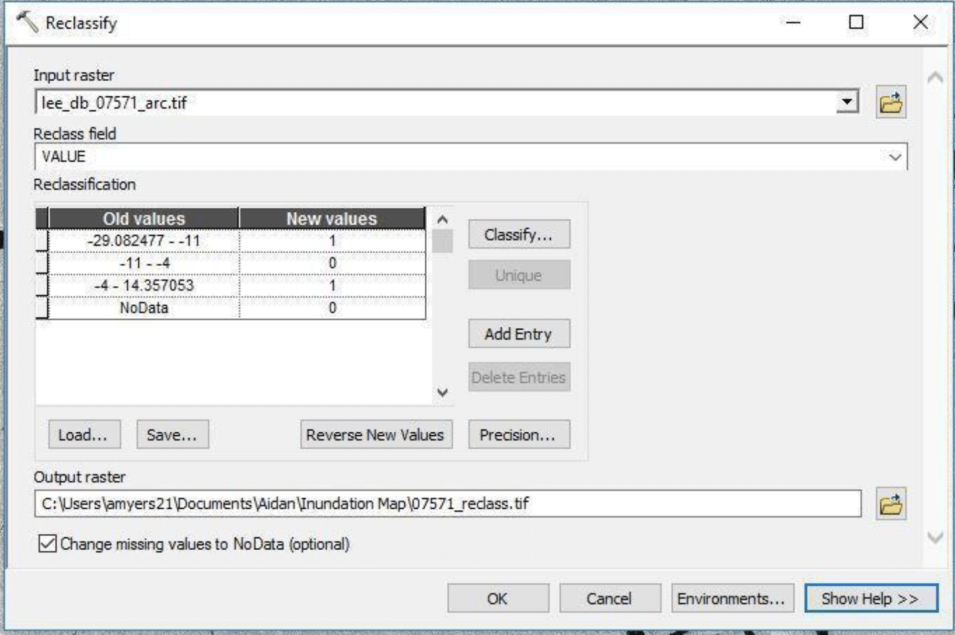
In this recipe, we describe methods used to (a) create an inundation image animation from 16 PALSAR RTC products and (b) produce an inundation map that quantifies the number of flooding events from the given set of data.
Source: Bruce Chapman, JPL, and Rick Guritz, ASF
Prerequisites
Part 1 Materials List
- ALOS PALSAR RTC products (see sample granules below)
- ArcMap (version 10.3 used in this recipe)
- Adobe Photoshop (CS6 used in this recipe)
Part 2 Materials List
- ArcMap
- Lee-filtered db images from Part 1: Generating an Inundation Animation.
Part 1: Generating an Inundation Animation
Download and Organize Data
Download data either by clicking the links to the sample granules (below) or by bulk downloading using the Vertex data portal.
- For help using Vertex to search for and download data, please refer to the Vertex Getting Started User Guide.
Organize data.
- Extract data from the downloaded .zip files and copy the HH image from each granule into a single HH frame folder.
Convert Images to Decibels
Convert the RTC images from linear power to db
- In ArcMap, load all of the RTC HH GeoTIFF images from the folder. If prompted to create pyramids for an image layer, click No.
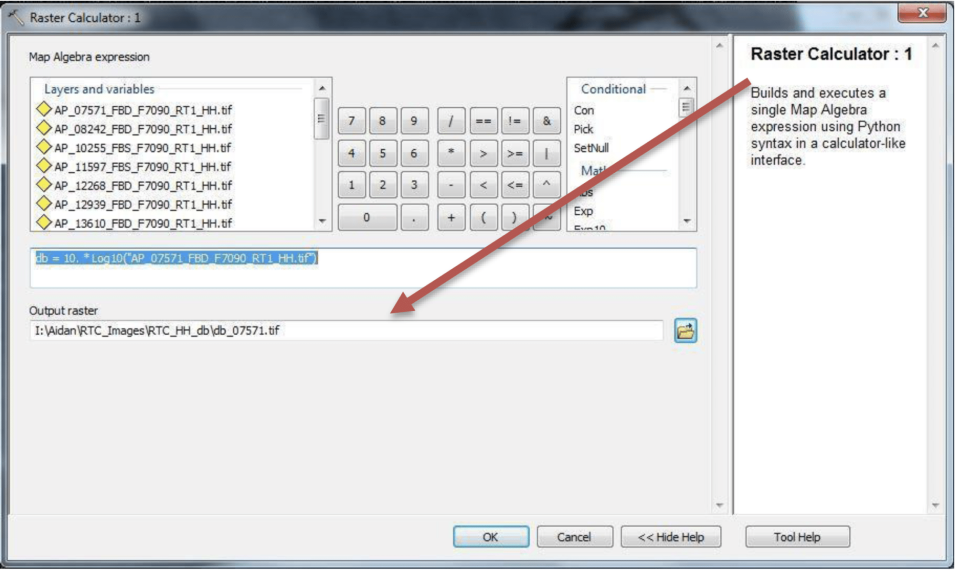
- Start the Raster Calculator tool (Spatial Analysis Tools > Map Algebra).
Note: Raster Calculator is part of the Spatial Analyst toolbox, which requires the Spatial Analyst license. - Create output folder HH_db, and specify output filename as Rnnnnn_db.tif where nnnnn is orbit number.
- Compute db = 10.*Log10 (“RTC_HH_granule”)
- Repeat process for all RTC granules.