Access a range of datasets and data tools to further your research in industrial emissions and greenhouse gases.
Since the industrial revolution in the mid-1800s, human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and the clearing of land for agriculture, have increased the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The planet's average surface temperature has risen about 2.12° Fahrenheit (1.18° Celsius) since the late 19th century, and 10 of the warmest years on record have been observed since 2014.
In its Sixth Assessment Report, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change concluded that it is unequivocal that the increase of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) in the atmosphere over the industrial era is the result of human activities and that human influence is the principal driver of many changes observed across the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere and biosphere.
Greenhouse Gases
Life on Earth depends on energy from the Sun. About half the light energy reaching Earth's atmosphere passes through the air and clouds to the surface, where it is absorbed and radiated in the form of infrared heat. Nearly 90% of this heat is then absorbed by greenhouse gases and re-radiated, slowing heat loss to space. GHGs include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), ozone (O3), and water vapor (H2O).
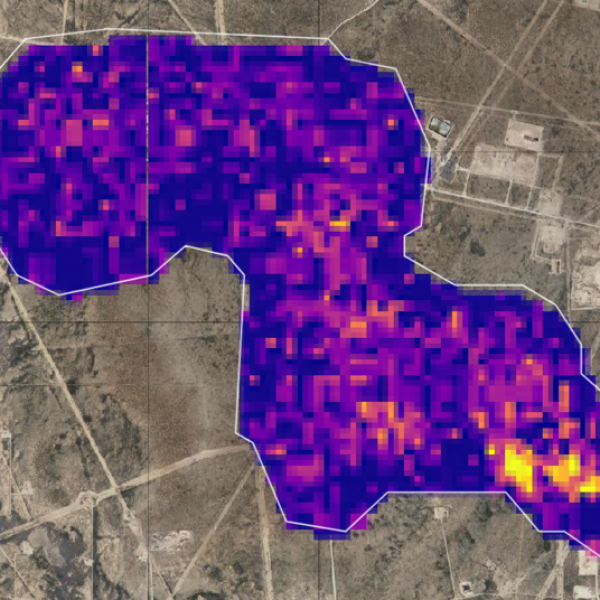
Remotely sensed greenhouse gas data, such as the data collected by NASA’s Earth-observing satellites, are used in atmospheric models to estimate the sources and sinks of these gases. These data allow researchers to pinpoint sources and hotspots of greenhouse gases across the globe. NASA also curates socioeconomic data to shed light on the health impacts of greenhouse gas emissions on people and communities. The U.S. Greenhouse Gas Center is a joint effort between NASA and other U.S. government agencies to open up access to trusted data on greenhouse gases.
Learn How to Use Industrial Emissions Data


Join Our Community of NASA Data Users
While NASA data are openly available without restriction, an Earthdata Login is required to download data and to use some tools with full functionality.
Learn About the Benefits of Earthdata LoginFrequently Asked Questions
Earthdata Forum
Our online forum provides a space for users to browse thousands of FAQs about research needs, data, and data applications. You can also submit new questions for our experts to answer.
Submit Questions to Earthdata Forumand View Expert Responses