Access a range of datasets and data tools to further your sulfur dioxide research.
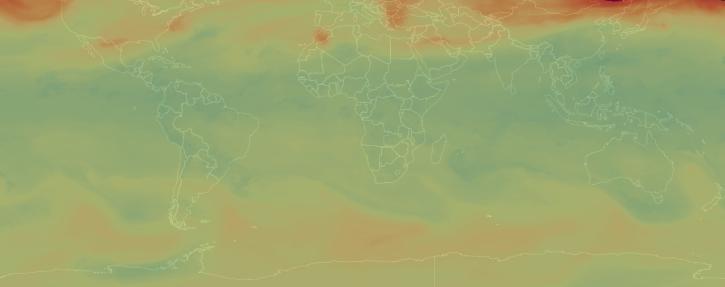
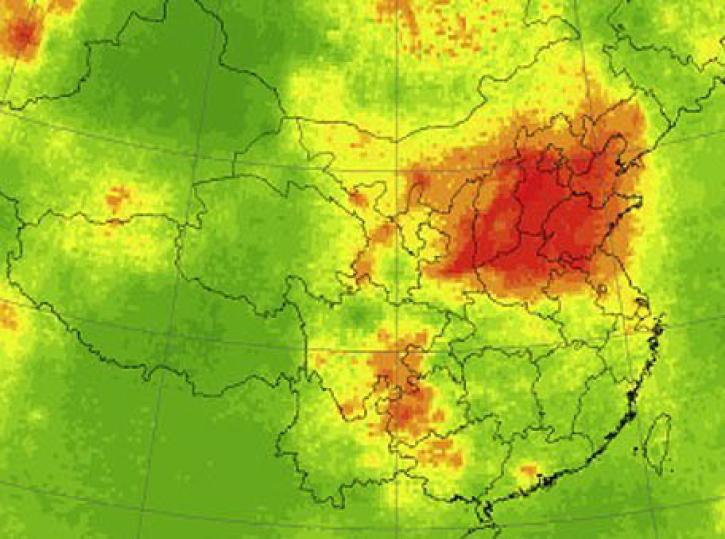
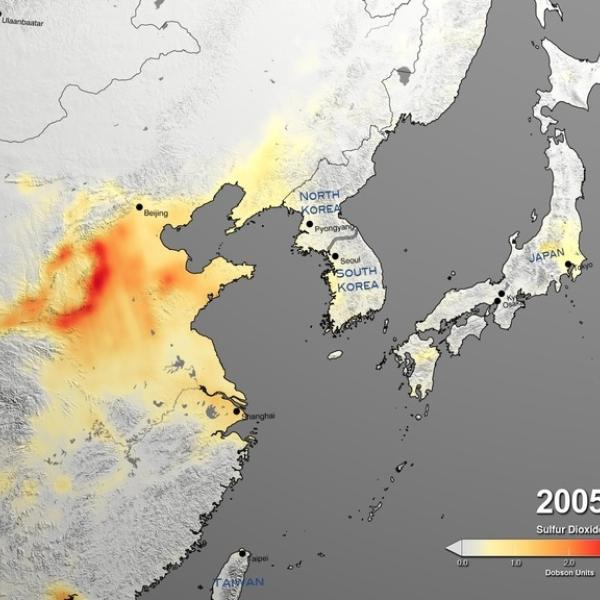
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a colorless, toxic gas that can irritate people’s airways when inhaled. Processes that emit sulfur dioxide include fossil fuel burning from power plants and industrial facilities, as well as natural volcanic eruptions. The third most abundant gas on our neighboring planet Venus, sulfur dioxide is considered a trace gas on Earth.
When sulfur dioxide reacts with water, ozone, and other molecules in the lower atmosphere, it creates particles that contribute to acid rain and haze. This can cause harm to human health, animals, vegetation, and crops. Higher up in the atmosphere, sulfur particles can increase the reflectance of clouds.
NASA’s Earth-observing instruments collect data on levels of sulfur dioxide and other trace gases in the atmosphere. These datasets can be used to monitor historical and near real-time global and regional emissions, allowing scientists to track volcanic activity and better study sulfur dioxide’s effects on the weather and human health.
Learn How to Use Sulfur Dioxide Data
Join Our Community of NASA Data Users
While NASA data are openly available without restriction, an Earthdata Login is required to download data and to use some tools with full functionality.
Learn About the Benefits of Earthdata LoginFrequently Asked Questions
Earthdata Forum
Our online forum provides a space for users to browse thousands of FAQs about research needs, data, and data applications. You can also submit new questions for our experts to answer.
Submit Questions to Earthdata Forumand View Expert Responses