Access a range of datasets and data tools to further your biosphere research.
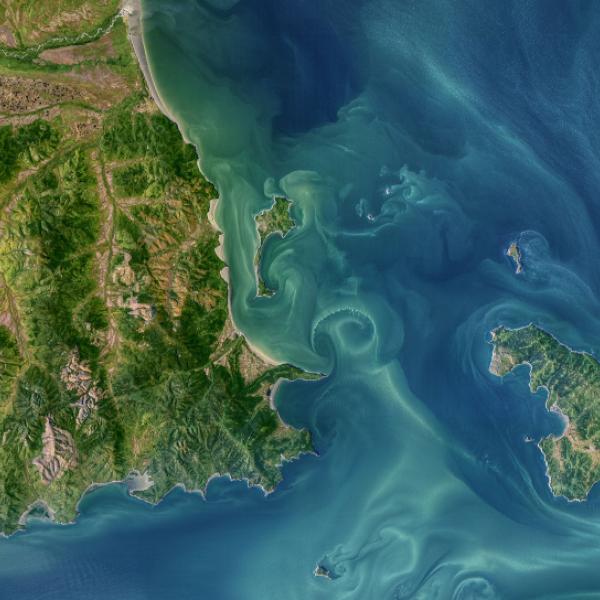
Life within Earth’s biosphere consists of millions of species living in various types of biomes such as grassland, forest, desert, aquatic, and tundra areas. Biomes are often divided into numerous subtypes, including rainforest or savannah. Vegetation, soil, climate, and wildlife are the primary components of a biome’s composition. Maintaining species richness in the biosphere ensures the productivity and stability of ecosystem processes, making it critical to monitor vegetation and wildlife health and prevent their loss.
NASA’s satellite-based and other remote sensing data measure vegetation condition (e.g., greenness, water stress), vegetation types, canopy height, vertical structure of forests, habitat structure, evaporative stress, delineation and conservation of protected areas, phenology, and biomass measurements of groups and individuals. There is data with environmental variables such as temperature and precipitation for species distribution and habitat suitability; human impacts to biological environments, such as deforestation or nighttime lights on predator-prey interactions; spectroscopy information for direct detection of species; thermal anomaly and fire detection signals; and aquatic data such as cyanobacteria indexes and water surface temperature.
Latest Biosphere News
Join Our Community of NASA Data Users
While NASA data are openly available without restriction, an Earthdata Login is required to download data and to use some tools with full functionality.
Learn About the Benefits of Earthdata LoginFrequently Asked Questions
Earthdata Forum
Our online forum provides a space for users to browse thousands of FAQs about research needs, data, and data applications. You can also submit new questions for our experts to answer.
Submit Questions to Earthdata Forumand View Expert Responses