Field Campaigns
ABoVE
ACT-America
AFRISAR
AIRMOSS
ASCENDS
ATom
AVIRIS
BioSCape
BOREAS
CARAFE
CARVE
COMEX
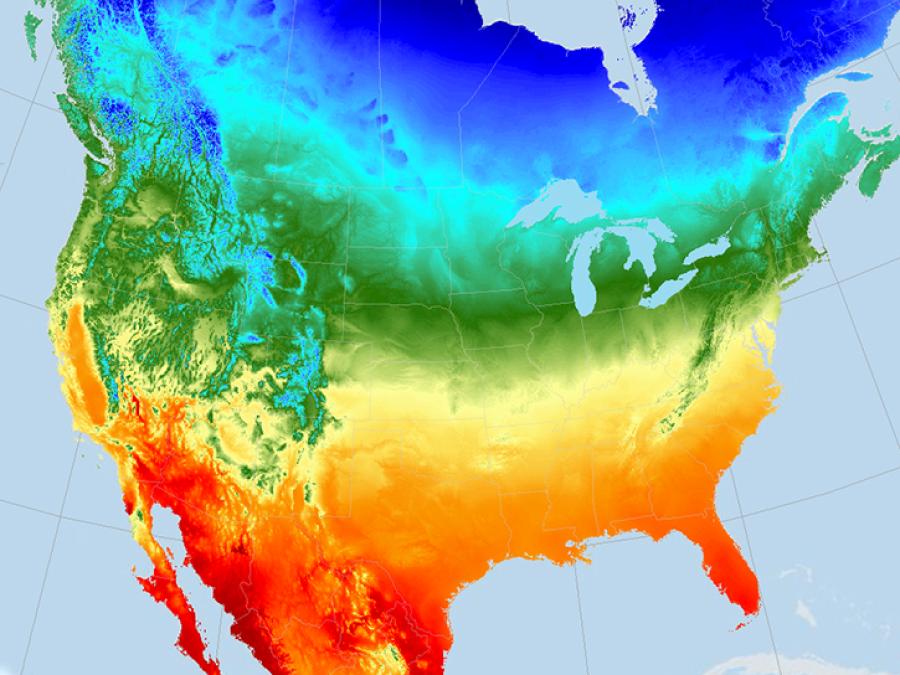
Daymet
Delta-X
FIFE
GEDI
GEMx
LBA-ECO
MASTER
OTTER
SAFARI 2000
SHIFT
SISTER
SNF

NASA's Oak Ridge National Laboratory Distributed Active Archive Center (ORNL DAAC) specializes in data and information relevant to terrestrial biogeochemistry, ecology, and environmental processes, which are critical to understanding the dynamics of Earth's biological, geological, and chemical components.
ORNL DAAC archives data and model products that were generated with funding from NASA's Terrestrial Ecology program and other programs within NASA's Carbon Cycle and Ecosystems focus area. Datasets are organized by both the name of the associated NASA project and by science themes in biogeochemical and ecological research.
The mission of ORNL DAAC is to assemble, distribute, and provide data services for a comprehensive archive of terrestrial biogeochemistry and ecological dynamics observations and models to facilitate research, education, and decision-making in support of NASA's Earth Science.
Our goals are to:
ORNL DAAC regularly partners with other Earth Observation System Data and Information System (EOSDIS) data centers and the following organizations towards shared goals.
The International Council for Science World Data System (ICSU WDS) promotes stewardship and access to data and data services across a range of science disciplines.
The Artic Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) Working Groups define standards of data management, services, models, variables, and products for ABoVE. ORNL DAAC staff participate in the Core Variables & Standards and the Geospatial Products & Standards groups.
The Earth Science Data System Working Groups (ESDSWG) is a NASA organization that focuses on the exploration and development of recommendations derived from pertinent community insights of NASA's heterogeneous and distributed Earth science data systems.
The Federation of Earth Science Information Partners (ESIP) is a networked community that brings together science, data, and information technology practitioners.
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) Core Science Systems (CSS) delivers natural science information to the United States in support of smart decisionmaking.
ORNL DAAC is a member of the ORNL Climate Change Science Institute (CCSI) and often contributes to its other data centers.
The Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Archive (ARM) provides observations to improve the understanding of clouds and aerosols.
The Next-Generation Ecosystem Experiments (NGEE Arctic) improve climate model predictions through advanced understanding of coupled processes in Arctic terrestrial ecosystems.
The Spruce and Peatland Responses Under Climatic and Environmental Change (SPRUCE) experiment assesses the response of northern peatland ecosystems to increases in temperature and exposures to elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations.
A preprint dataset is one which is made available prior to the completion of the ORNL DAAC's quality assurance and documentation work. This is most often done to support the peer review process for journal articles involving the data. As with a journal preprint, a preprint dataset includes the materials as received from the data provider, is subject to revision, and should be used as one would a journal preprint. Preprint datasets at the ORNL DAAC are not visible in NASA's Earthdata Search, and the ORNL DAAC attempts to prevent them from showing up in Internet search tools. Any differences in the finalized data relative to the data from the preprint version will be described in the finalized dataset documentation.
NASA facility instruments operate out of a NASA research center and support multiple science disciplines, field investigations, and NASA science objectives. Facility instruments are supported by managers in the Earth Science Division (ESD) Research and Analysis Program, and/or the Earth Observation System (EOS) Project Science Office.
| Title | Platform | Type | Measurements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airborne Visible and InfraRed Imaging Spectrometer - 3 (AVIRIS-3) | Spectrometer | Radiance from the surface and atmosphere | |
| Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS-C) | Spectrometer | Imagery | |
| Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer 5 (AVIRIS-5) | Spectrometer | Radiance from the surface and atmosphere | |
| Enhanced MODIS Airborne Simulator (eMAS) | Spectrometer | Imagery | |
| Land, Vegetation and Ice Sensor (LVIS) | Lidar | Vegetation; Vegetation structure; surface topography; ice and sea ice elevations; ocean surface topography | |
| MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator (MASTER) | Spectrometer | Imagery | |
| National Airborne Sounder Testbed - Interferometer (NAST-I) | Interferometer | Temperature; Relative Humidity | |
| Next-Generation Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS-NG) | Spectrometer | Imagery | |
| Pushbroom Imager for Cloud and Aerosol Research and Development (PICARD) | Spectrometer | Imagery | |
| Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar (UAVSAR) | Radar | Imagery |
We are proud to be a CoreTrustSeal Certified Repository. CoreTrustSeal is an international, community based, non-governmental, and non-profit organization promoting sustainable and trustworthy data infrastructures.
